SAS具有多种内置函数,有助于分析和处理数据。 这些函数用作DATA语句的一部分。 它们将数据变量作为参数,并将结果存储到另一个变量中。 根据函数的类型,所需的参数数量可能会有所不同。 一些函数接受零参数,而另一些函数接受固定数量的变量。 以下是SAS提供的功能类型列表。
句法
在SAS中使用函数的一般语法如下。
FUNCTIONNAME(argument1, argument2...argumentn)
这里的参数可以是常量,变量,表达式或另一个函数。
功能分类
根据它们的使用情况,在SAS中的功能被分类为如下。
- 数学
- 日期和时间
- 字符
- 舍去
- 杂
数学函数
这些是用于对变量值应用一些数学计算的函数。
例子
下面的SAS程序显示了一些重要的数学函数的使用。
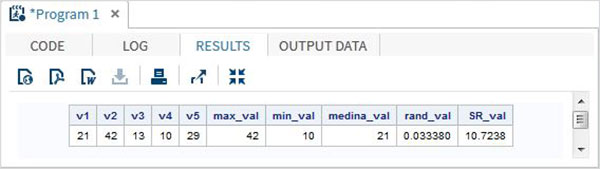
data Math_functions; v1=21; v2=42; v3=13; v4=10; v5=29; /* Get Maximum value */ max_val = MAX(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5); /* Get Minimum value */ min_val = MIN (v1,v2,v3,v4,v5); /* Get Median value */ med_val = MEDIAN (v1,v2,v3,v4,v5); /* Get a ranDOM number */ rand_val = RANUNI(0); /* Get Square root of sum of the values */ SR_val= SQRT(sum(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5)); proc print data = Math_functions noobs; run;
当上面的代码运行时,我们得到以下输出:
日期和时间函数
这些是用于处理日期和时间值的函数。
例子
下面的SAS程序显示了使用日期和时间的函数。
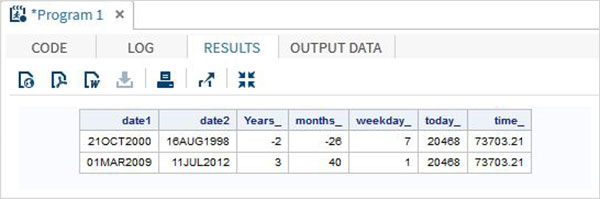
data date_functions;
INPUT @1 date1 date9. @11 date2 date9.;
format date1 date9. date2 date9.;
/* Get the interval between the dates in years*/
Years_ = INTCK('YEAR',date1,date2);
/* Get the interval between the dates in months*/
months_ = INTCK('MONTH',date1,date2);
/* Get the week day from the date*/
weekday_ = WEEKDAY(date1);
/* Get Today's date in SAS date format */
today_ = TODAY();
/* Get current time in SAS time format */
time_ = time();
DATALINES;
21OCT2000 16AUG1998
01MAR2009 11JUL2012
;
proc print data = date_functions noobs;
run;
当运行上面的代码,我们得到以下的输出:
字符函数
这些都是用于处理字符或文本值的功能。
例子
下面的SAS程序显示了使用的字符函数。
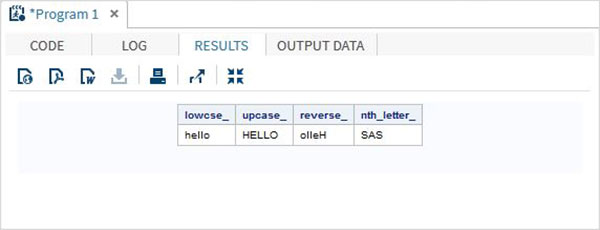
data character_functions;
/* Convert the string into lower case */
lowcse_ = LOWCASE('HELLO');
/* Convert the string into upper case */
upcase_ = UPCASE('hello');
/* Reverse the string */
reverse_ = REVERSE('Hello');
/* Return the nth word */
nth_letter_ = SCAN('Learn SAS Now',2);
run;
proc print data = character_functions noobs;
run;
当运行上面的代码,我们得到以下的输出:
截断功能
这些是用于截断数字值的功能。
例子
下面的SAS程序说明了如何使用截断功能。
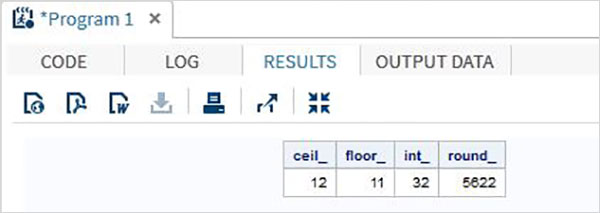
data trunc_functions; /* Nearest greatest integer */ ceil_ = CEIL(11.85); /* Nearest greatest integer */ floor_ = FLOOR(11.85); /* Integer portion of a number */ int_ = INT(32.41); /* Round off to nearest value */ round_ = ROUND(5621.78); run; proc print data = trunc_functions noobs; run;
当运行上面的代码,我们得到以下的输出:
其它功能
例子
下面的SAS程序显示了使用的辅助功能。
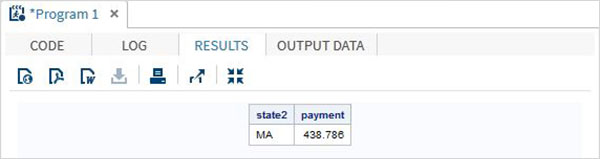
data misc_functions;
/* Nearest greatest integer */
state2=zipstate('01040');
/* Amortization calculation */
payment=mort(50000, . , .10/12,30*12);
proc print data = misc_functions noobs;
run;
当运行上面的代码,我们得到以下的输出: